At the same time, you need to keep it safe—for you and your user. Personalization is a great power and, as the popular Marvel hero says, with great power comes great responsibility.
This is what B2B marketing personalization is about.
What Is B2B Marketing Personalization?
B2B marketing personalization is the process of tailoring marketing efforts to the specific needs and preferences of other businesses.
In simple terms, it means customizing your marketing messages and content to make them more relevant and appealing to the companies you want to sell to.
This could include anything from sending personalized email campaigns by addressing recipients by name to creating specific content that answers specific needs.
The ultimate goal of B2B marketing personalization is to enhance audience engagement, leading to increased sales.
B2B marketing personalization benefits
Needless to say, B2B marketing personalization comes with many benefits—here are the most notable ones.
Better engagement. Like any personalization, personalized marketing messages make it easier for your audience to connect with your brand. When you address their uniqueness, your audience also regards you as a unique brand.
Increased conversions. Personalization works across the growth funnel. Accordingly, besides helping with engagement, it can also lead to higher conversion rates because it guides potential customers toward the products or services that meet their specific requirements.
Enhanced customer loyalty. Customer retention is vital to B2B, as B2B involves ongoing contracts and repeat business. Personalization is about creating stronger connections and those connections can help foster a sense of loyalty, creating lasting long-term relationships.

Efficient use of resources. On a more practical side, personalized marketing helps you allocate your marketing resources more effectively. Personalization means focusing on a narrower audience thus fewer people. This results in less wasted content and campaigns for people who wouldn’t be interested in what you offer in the first place.
Valuable data insights. Personalized marketing often involves segmenting your customer base into smaller groups based on your criteria. And with the power of data analysis, you can optimize these segments.
For example,
- Retailers segment their customers based on their past purchases and browsing behavior.
- Companies often segment their email lists based on open and engagement rates.
- Hotel chains segment their loyalty program members based on factors like the frequency of stays, preferred locations, and spending habits.
- Specifically in B2B, companies often employ Account-Based Marketing strategies, according to which they segment their target accounts based on industry, company size, and specific pain points.
B2B vs B2C Marketing Personalization
B2B marketing is different from B2C in many aspects. On the one hand, B2B targets professionals who are looking for solutions that will help them with their work. On the other hand, B2C is about reaching out to individuals who want to satisfy their consumer needs.
When it comes to personalization, B2B personalization involves tailoring content and solutions for a select group of businesses and decision-makers. In this case, the average potential customer has complex needs and longer sales cycles.
Regarding B2C, businesses have a much larger and diverse customer base. Personalization is more about mass customization and emotionally-driven content that will help with quick purchasing decisions.
To sum up, the complexity of B2B transactions, the need to address a variety of decision-makers, and the emphasis on long-term relationships make personalization a critical component of a successful B2B marketing strategy.
Types of B2B Marketing Personalization
Website Content Personalization
In this type of personalization, the company’s content can change when the kind of user also changes.
In theory, dynamic content allows you to create tailored website experiences for your visitors. Its power lies in delivering the right message to the right audience at the right time. Dynamic content involves customizing website content in real-time based on the specific characteristics and behavior of the user.
In practice, dynamic content works in 4 steps:
- Visitor data collection. To make dynamic content work, you need to gather data about your website visitors. This data can include information such as type of industry, company size, location, past website interactions, and more. The more data you collect, the more options for personalization you have.
- Segmentation. Once you have collected visitor data, you can segment your audience into different groups based on criteria that make the most sense for your business
- Content variations. For each segment, you can create multiple variations of content. These variations can include different headlines, images, text, calls to action (CTAs), and even entire sections of a webpage.
- Real-time personalization. When a visitor lands on your website, the dynamic content changes according to the segment the visitor belongs.

For example, this is how HubSpot, the well-known CRM, utilizes dynamic content. When first-time visitors arrive at HubSpot’s website, they are often shown introductory content explaining the benefits of inbound marketing and how HubSpot can help. However, for returning visitors or users with specific interactions in their history, the content changes. So, if a visitor has previously downloaded an eBook on email marketing, HubSpot may display content that promotes advanced email marketing tools and features.
Email Marketing Personalization
If there is one marketing channel that comes to mind when you hear the word “personalization”, then this has to be email. As email is considered one of the most personal digital channels, email marketing is traditionally more tailor-made.
A few key elements of email marketing personalization include:
- Recipient’s name
- Email content
- Subject lines
- Behavior-based triggers
- Calls to Action (CTAs)
As an email marketing personalization example, let’s consider Salesforce, another popular CRM platform. For this instance, let’s assume that there’s a website visitor who has an interest in two distinct Salesforce products: “Sales Cloud” and “Service Cloud.”
Using dynamic content and personalization, Salesforce can send this contact an email with the following characteristics:
- Subject line. The subject line might read, “Unlock Your Sales and Service Potential with Salesforce.”
- Header. The email header can feature a personalized greeting, such as “Hello, Sales Professional!” or “Hello, Service Expert!”
- Body. The email body can include content sections highlighting the benefits of Sales Cloud and Service Cloud, tailored to the recipient’s interests.
- Calls to Action (CTAs). Personalized CTAs within the email encourage the contact to explore the specific product solutions they’ve shown interest in.
Social Media Personalization
B2B social media personalization is about tailoring social media content and interactions. This can involve sharing industry-specific insights, thought leadership, and case studies relevant to their needs.
Here are a few social media personalization examples for B2B to inspire you:
LinkedIn. We’re starting off with the most B2B social media platform of all. A B2B professional on LinkedIn can send personalized connection requests to potential business partners. If they want to make it more personal, instead of sending a generic connection request, they can tailor each request with a note that mentions common interests, a shared connection, or specific industry insights.
Twitter. Your average B2B tech company on Twitter has followers from various industries. So what they can do is use Twitter lists, now X lists, to segment their audience by industry. When they share industry-specific news, trends, or articles, they can tag or mention the relevant industry followers in their posts. For instance, when sharing a healthcare-related article, they can mention healthcare professionals and engage them in industry-specific conversations.
YouTube. Let’s say that a B2B training company uses YouTube to promote its instructional content. They can create customized playlists on their channel, each focused on a specific topic or industry. For example, they can have separate playlists for “IT Training” and “Sales Techniques.”
Advertising Personalization
When B2C brands want to advertise, they usually do so through above-the-line advertising; mostly TV, radio, and print. In the case of B2B, below-the-line advertising is what actually works—specific audiences need specific messages.
When it comes to advertising options, each advertising platform has its own customization options but let’s take Google Ads as an example. We’ll use GrowthRocks, our growth hacking agency for this one.
In GrowthRocks, we use a number of different digital marketing services for a number of different kinds of businesses. Accordingly, a potential client could be an established eCommerce business. At the same time, another potential client could be a tech startup in its infancy. If we wanted to create an engaging for each business, we’d better have different messaging with industry-specific copy.
For example, in the first case, the ad copy in the Google Ad would read“3X Your Online Sales with Tailored eCommerce Marketing Solutions”. In the second one, the copy would read something along the lines of “Accelerate Your Tech Startup’s Growth with Our Digital Marketing Expertise”.
Personalization vs Data Privacy
Balancing personalization with data privacy is not only essential for ethical marketing but also for complying with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy laws.
Here’s what you should know and some hands-on advice with examples.
Consent & Transparency
You need to obtain clear and unambiguous consent from users for data collection and personalization. Provide opt-in options for personalization features, making it easy for users to understand what they’re consenting to.
For example, when users sign up for your newsletter, include a checkbox that asks if they want to receive personalized content or recommendations. Also, don’t forget to provide a clear link to your privacy policy for transparency.
Another typical case is cookie consent.
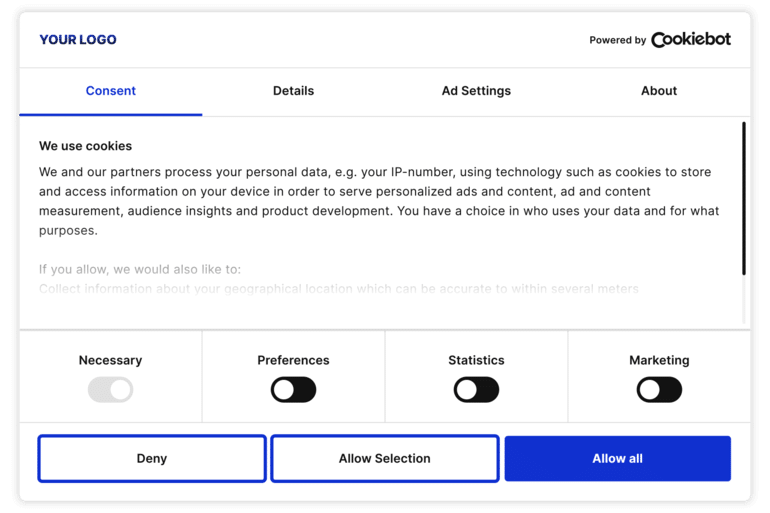
On the user’s first visit, show a banner with a message about using cookies for a better shopping experience and personalized recommendations. Also, provide “Accept” and “Manage Preferences” buttons. “Accept” enables personalization and functionality cookies. “Manage Preferences” leads to a settings page for users to choose cookie types, each with explanations. Lastly, link to the privacy policy for more info, allowing users to make informed choices and adjust cookie preferences.
Data minimization
Data minimization means collecting only the data necessary for personalization and nothing more. Additionally, you will have to limit the data you collect to reduce the risk of breaches and respect user privacy.
You might only collect data like purchase history and browsing behavior to offer personalized product recommendations. At the same time, avoid collecting sensitive data unrelated to personalization, such as financial data, health information, racial or ethnic background, and religious beliefs.
Security measures
Invest in robust data security measures, including encryption and secure storage, to protect user data from breaches. Some of the most common measures include:
- Keep themes and plugins updated. Outdated software is a common entry point for hackers.
- Install security plugins. Use security plugins like Wordfence, Sucuri, or iThemes Security to help monitor and protect your site from threats.
- Limit login attempts. Install a plugin that limits the number of login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA). To add an extra layer of security for logins, enable two-way authentication (2FA) passwordless authentication such as magic links.
- Secure hosting. Choose a reputable hosting provider that offers strong security features and good customer support.
- Protect wp-config.php. If you are using WordPress, restrict access to your wp-config.php file, which contains sensitive information. by using .htaccess rules to limit access to this file.
- Change the default admin username. Avoid using “admin” as the username for your administrator account, as it’s a common target for attacks.
Anonymization & Pseudonymization
It’s always a good idea to anonymize or pseudonymize user data whenever possible to protect privacy while enabling personalization.
Anonymizing is effectively stripping data of any personally identifiable information (PII) so that it cannot be linked back to a specific individual. This is typically achieved by removing or replacing sensitive information, such as names, email addresses, or phone numbers, with random or generic identifiers.
On the other hand, pseudonymizing involves replacing direct identifiers (e.g., a name) with a pseudonym, which is a unique but non-identifying code or identifier. Unlike anonymization, pseudonymization retains the potential for re-identifying individuals.
For example, if you’re conducting A/B testing on your website, you can use pseudonymized user IDs rather than personally identifiable information to track users’ interactions.
Conclusion
B2B marketing personalization is a lot more than addressing the user with their first name.
However, no matter what kind of digital personalization you want to experiment with, you need to balance between personalization and data privacy.
And if your website is accessible to EU and Californian users, you will most definitely need to ensure GDPR and CCPA compliance respectively.
If you need help with your GDPR/CCPA compliance, we can handle all privacy and legal jargon and we will take care of:
- Auditing your touchpoints
- Proposing ways to comply with GDPR/CCPA
- Documenting your processes, data flows, and digital assets
Until next time – keep your marketing personal, and safe. And if you need any help with your B2B marketing, we are a B2B marketing agency with tons of experience. So let us know!

I write for GrowthRocks, one of the top growth hacking agencies. For some mysterious reason, I write on the internet yet I’m not a vegan, I don’t do yoga and I don’t drink smoothies.